The economy in Germany
Why is the German economy so strong? Why is Germany’s gross national product so high? Find all the important answers to your questions here, alongside further information about Germany’s economic power.
#LeadingInnovation – the important sectors
European Patent Index 2024
- 48 : USA
- 25 : Germany
- 21 : Japan
- 20 : China
Is Germany’s economic power generated only by exports?
Germany is a major exporter – but exports are not everything. Let us explain why Germany is a developed country, what type of economy Germany has and which factors make Germany’s economy so strong. One important role is played by German industry. Industry accounts for 26.6 percent of gross value added in Germany – this is the highest figure of all the G7 countries. The strongest sectors are vehicle manufacturing, electronics, mechanical engineering and the chemical industry. Alongside China and the USA, Germany is one of the world’s three largest export nations. In 2022, Germany exported goods worth 1,576 billion euros. The export quota was 50.3 percent. Germany’s true strength lies elsewhere, however: small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), known in Germany as the Mittelstand, are the beating heart of the German economy. This refers to the 99.6 percent of companies in Germany that have an annual turnover of below 50 million euros and employ fewer than 500 people. Nearly 1,000 of them are so-called hidden champions, world market leaders of which the public is hardly aware.
Quick facts
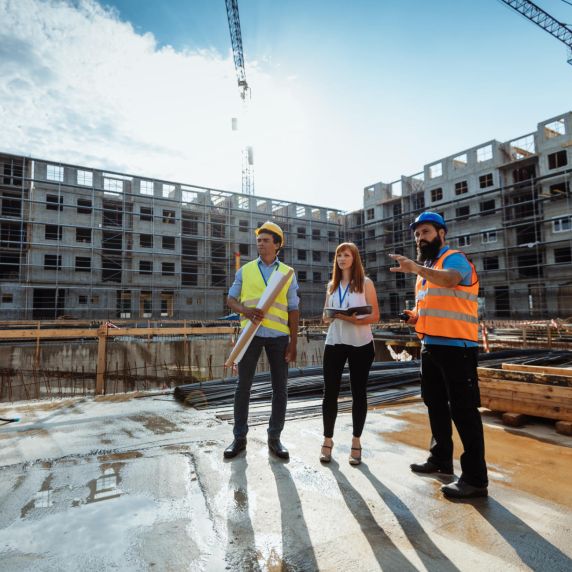
Is industry important for Germany?
Industry accounts for a large proportion of economic output in Germany and thus serves as the foundation for growth and prosperity to a much greater extent than in many other industrialised countries. Four areas dominate the manufacturing sector in terms of turnover and workforce size: the automotive, mechanical engineering, chemical and electronic industries. These sectors are associated with traditional companies of global renown such as Mercedes-Benz, Siemens, BASF or Bosch. However, there are also extremely successful new businesses like the pharmaceutical firm Biontech, which was one of the few companies to place a highly effective coronavirus vaccine on the market.
Is Germany’s economy innovative?
The innovations of today create the world of tomorrow. One of Germany’s greatest strengths is therefore its innovative and high-performing economy. It is the country with the most patent applications in Europe and ranks fifth worldwide. Start-ups play an important role in Germany: Berlin is considered to be one of the world’s leading start-up ecosystems. The innovative capacity of start-ups is also vital when it comes to future-proofing German industry. Research, digitisation and artificial intelligence are all extremely important in this context.
Investment in research and development
- 26 : Automotive industry
- 9 : Electrical industry
- 7.2 : Mechanical engineering
- 5.5 : Pharmaceutical industry and ICT
#EconomyInTransition
What role does Germany play in global trade?
Judging by how important foreign trade is to the country’s gross domestic product (GDP), Germany has the most open economy of the G7 states. Its trade-to-GDP ratio is 98.6 percent – this refers to the sum total of imports and exports in relation to GDP. Germany relies on and promotes free exchange between countries and is committed to open and equal relations with all countries. Alongside China and the USA, Germany is one of the world’s three largest export nations.
Is artificial intelligence important for the German economy?
The use of artificial intelligence is enabling digitisation to take a crucial new step forward. With major research associations such as the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, which pursues practice- and application-oriented research, Germany is a leader in areas such as the deployment of artificial intelligence and machine learning in industrial production. The term Industry 4.0 describes the fourth industrial revolution, based on the vision of a data-controlled, networked and AI-supported smart factory.
Does sustainability play a role in the German economy?
Climate change poses such a threat to the foundations of our prosperity and growth that only a sustainable economy will survive in the future. This also applies to industry, and therefore especially to an energy-dependent industrialised country like Germany. Thanks in part to the government’s German Sustainable Development Strategy (GSDS), industrial companies in Germany already lead the field internationally with their energy- and resource-efficient, low-polluting technologies, systems and products. Roughly half of the country’s electricity is already generated using renewable sources. Through its energy transition, Germany is making an active contribution to the fight against climate change and to implementing the Paris Agreement. The goal is to reach climate neutrality by 2050. In this respect, protecting the climate and sustainability go hand in hand – in the best interests of our planet.
Is health an important sector in the German economy?
Innovations help people – this is clearly evident in the healthcare sector. Without strong research, vaccines against the coronavirus could never have been developed in such a short period of time. And without a flexible industry, millions of vaccine doses could not have been produced so quickly. Germany’s healthcare sector is efficient and capable in many areas: from pharmaceuticals research and the production of drugs to laboratory equipment and high-precision medical technology.
Medical technology exports are a little known success story for Germany. With a market share of more than 25 percent, Germany is Europe’s most important manufacturer of medical technology. Within Germany, the state of Baden-Württemberg is the most important region, accounting for over 25 percent. It is also home to the small town of Tuttlingen with its 35,000 inhabitants, which is a global centre for medical technology.
Is training important for Germany’s strong economy?
Well-trained employees form the backbone of any productive and high-tech economy. That’s why Germany has 324 recognised occupations requiring formal training in industry and the skilled crafts, in the civil service, home economics, agriculture, shipping and the “liberal professions”. These occupations have defined courses of training that culminate in an exam. Training takes place partly in a company, partly in different companies, and partly at a vocational school with instruction in technical and general subjects: this is how Germany’s world-renowned dual vocational training system works. In this way, trainees learn all the skills necessary for an occupation and thereby lay the foundation for a wide-ranging professional career. The dual system is so successful that it has already been adopted by many countries.
Would you like to work in the German economy?
Germany has one of the world’s largest and most stable economies. For years there have been many job vacancies that it has proven impossible to fill. Demographic shifts and an ageing population are further exacerbating the skilled labour shortage. Germany is therefore reliant on skilled migrant workers and at the same time is an attractive destination for workers from all over the world.
How diverse is the economic environment in Germany?
A tolerant and diverse working environment is the foundation for a productive and future-proof economy. One important role in this is played by flexible working hours, employee-friendly workplaces and other New Work trends. German companies are just as progressive and future-oriented in these areas as they are when it comes to technical innovations.
What role does diversity play in the German economy?
More than 3,500 public and private employers with a total of 13.4 million employees have signed up to the “Diversity Charta” to achieve equal workplace opportunities.
More information can be found here: Diversity Charta.
Why is Germany’s gross domestic product so high?
GDP refers to all the goods and services produced by an economy. Thanks to its strong economy, Germany ranks fourth worldwide in terms of GDP, after the USA, China and Japan. When calculating GDP, everything that is produced in a defined period is factored in. Furthermore, GDP includes the value of services, consuming spending, construction investment and corporate investments in things like machines and vehicles. All sectors of the economy are taken into account. Another component is the so-called balance of trade – that is to say the difference between the value of goods that companies sell abroad (exports) and buy from there (imports).
What does Germany do to promote a fair global economy?
Many millions of people around the world suffer because they are badly paid for their work. In many cases minimum social standards and human rights are ignored, such as the ban on forced and child labour. Germany has set itself the political goal of bringing about a fair global economy. It has adopted a National Action Plan for Business and Human Rights (NAP) and, through its Supply Chain Act, has obliged companies to ensure minimum standards within their respective sphere of influence.